Understanding Bitcoin Cycles: A Comprehensive Guide
Uncover the secrets of Bitcoin’s wild price swings! Learn to navigate the volatile Bitcoin cycles and understand the factors driving its dramatic ups and downs. Master technical analysis and psychological insights to make informed decisions in this exciting, yet risky, market.
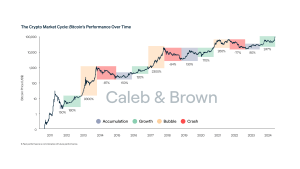
The Bitcoin cycle, characterized by its dramatic price swings and periods of intense volatility, presents both significant opportunities and substantial risks. Understanding its nuances is crucial for anyone considering involvement in the cryptocurrency market. This involves more than just tracking the price; it demands a deep understanding of the underlying factors driving these cycles. We’ll delve into the historical patterns, technical analysis, and psychological influences that shape the Bitcoin landscape. This comprehensive guide aims to provide a clear and insightful overview, equipping you with the knowledge to navigate this dynamic market effectively.
The Historical Perspective: Bitcoin’s Ups and Downs
Since its inception, Bitcoin has experienced a series of dramatic price fluctuations. From its humble beginnings as a niche digital currency, it has risen to global prominence, becoming a household name synonymous with cryptocurrency. Each cycle, typically lasting several years, has followed a similar pattern: a period of rapid growth, a peak, a significant correction, and then a period of consolidation before the next surge. Analyzing these past cycles provides valuable insights into potential future trends, although it’s crucial to remember that past performance is not indicative of future results. The unpredictable nature of the market makes precise predictions impossible, highlighting the importance of prudent risk management strategies.
Early Days and Initial Growth
The early days of Bitcoin were marked by slow, organic growth. Adoption was limited, and the price remained relatively low. This period established the foundational technology and built the initial community of users and developers. The slow and steady growth laid the groundwork for the explosive growth phases that were to follow, showcasing the power of decentralized technology and the potential for disruptive innovation.
The First Major Bull Run
The first major bull run, starting around 2013, saw Bitcoin’s price skyrocket, capturing the attention of mainstream media and attracting a wave of new investors. This period was characterized by intense speculation and rapid price increases, leading to significant gains for early adopters. However, it was also followed by a sharp correction, highlighting the inherent volatility of the market. This volatility underscores the need for careful consideration before investing any significant amount of capital.
Subsequent Cycles and Market Maturation
Subsequent cycles followed a similar pattern, with periods of intense growth interspersed with significant corrections. Each cycle brought increased sophistication to the market, with the emergence of new technologies, regulatory frameworks, and investment vehicles. This continuous evolution has gradually shifted the perception of Bitcoin, from a fringe technology to a potentially significant asset class, albeit one with significant volatility.
Technical Analysis: Chart Patterns and Indicators
Technical analysis is a crucial tool for understanding the Bitcoin cycle. By examining price charts and using various technical indicators, traders can identify potential trends, support levels, and resistance levels. This allows for more informed decision-making, although it’s important to remember that technical analysis is not a foolproof method, and its interpretations are subjective.
Key Indicators to Watch
- Moving Averages: These smooth out price fluctuations and help identify trends.
- Relative Strength Index (RSI): This measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions.
- MACD (Moving Average Convergence Divergence): This identifies changes in momentum by comparing two moving averages.
- Volume: High volume confirms price movements, while low volume suggests weak trends.
Understanding how these indicators interact and interpreting their signals requires practice and experience. Many resources are available online to assist in learning technical analysis, but it’s important to note that relying solely on technical analysis can be risky. A holistic approach combining various forms of analysis is generally recommended.
Psychological Factors: Fear, Greed, and Market Sentiment
The Bitcoin cycle is heavily influenced by human psychology. Fear and greed drive market sentiment, leading to periods of irrational exuberance and panic selling. Understanding these psychological factors is essential for navigating the market effectively. Market sentiment can shift rapidly, influencing price movements independent of fundamental changes.
The Role of Media and Social Influence
News coverage and social media significantly impact market sentiment. Positive news can trigger buying frenzies, while negative news can spark sell-offs. This highlights the importance of critical thinking and avoiding emotional decision-making. It’s crucial to filter information and form your own informed opinion, rather than relying solely on sensational headlines or social media trends.
Fundamental Analysis: Assessing Bitcoin’s Intrinsic Value
While technical analysis focuses on price patterns, fundamental analysis assesses the underlying value of Bitcoin. This involves considering factors such as adoption rates, network security, regulatory developments, and technological advancements. Fundamental analysis provides a longer-term perspective, helping to distinguish between short-term fluctuations and long-term trends.
Key Fundamental Factors
- Network Hash Rate: A measure of the computational power securing the Bitcoin network.
- Adoption Rate: The growth in the number of users and businesses accepting Bitcoin.
- Regulatory Landscape: Government regulations and policies affecting Bitcoin’s use and trading.
- Technological Advancements: Innovations within the Bitcoin ecosystem that enhance its functionality.
By carefully analyzing these fundamental factors, investors can gain a better understanding of Bitcoin’s long-term potential and make more informed investment decisions. However, it’s important to remember that even with strong fundamentals, the price can still be influenced by short-term market sentiment and speculative trading.
Risk Management: Protecting Your Investment
Investing in Bitcoin carries significant risk. Its volatile nature necessitates a robust risk management strategy. This includes diversifying your portfolio, only investing what you can afford to lose, and setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Furthermore, understanding the various forms of risk is paramount.
Types of Risk
Investors face several types of risk, including market risk (price volatility), regulatory risk (changes in government regulations), operational risk (security breaches or platform failures), and liquidity risk (difficulty selling your Bitcoin quickly). Understanding these risks and implementing strategies to mitigate them is vital for successful long-term investment.
Navigating the Bitcoin cycle requires a holistic approach, combining technical and fundamental analysis with a strong understanding of psychological factors and risk management principles. While potential rewards are substantial, so are the risks. Thorough research, careful planning, and disciplined execution are essential for success. Remember, no investment strategy guarantees profits, and informed decision-making is crucial in this dynamic and often unpredictable market. Continuous learning and adaptation are vital for long-term success in the cryptocurrency space. The inherent volatility necessitates a cautious approach, tempered by realistic expectations.