Understanding and Strategies in Options Trading
Unlock the secrets of stock options trading! Learn to navigate the complexities, understand the risks, and potentially reap huge rewards. Start your options trading journey today!
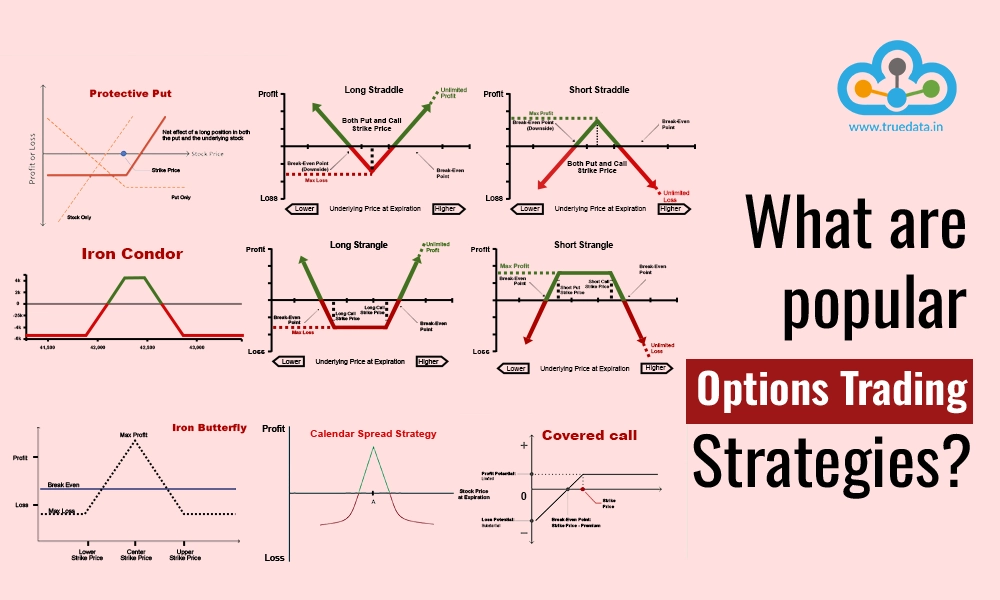
Stock option trading is a complex yet potentially lucrative financial instrument. It allows investors to buy or sell the right‚ but not the obligation‚ to buy or sell an underlying asset (typically a stock) at a predetermined price (the strike price) on or before a specific date (the expiration date). Understanding this fundamental concept is crucial before venturing into this dynamic market. Options trading offers both significant risk and reward‚ demanding a thorough understanding of market mechanics and risk management strategies.
Understanding the Basics of Options Contracts
At its core‚ an options contract is an agreement between two parties: the buyer and the seller. The buyer acquires the right‚ but not the obligation‚ to exercise the option. The seller‚ on the other hand‚ is obligated to fulfill the contract if the buyer chooses to exercise it. This asymmetry creates a unique risk-reward profile that differentiates options from traditional stock trading.
Call Options vs. Put Options
There are two main types of options contracts: call options and put options. A call option grants the buyer the right to buy the underlying asset at the strike price. A put option grants the buyer the right to sell the underlying asset at the strike price. The choice between a call or put option depends on the investor’s market outlook.
For instance‚ if an investor believes the price of a stock will rise‚ they might buy a call option. Conversely‚ if they believe the price will fall‚ they might buy a put option. The potential profit or loss for each type of option differs significantly‚ influenced by factors like time decay and market volatility.
Key Terminology in Options Trading
- Strike Price: The price at which the underlying asset can be bought or sold.
- Expiration Date: The date on which the option contract expires.
- Premium: The price paid by the buyer to acquire the option.
- Underlying Asset: The asset on which the option is based (usually a stock).
- In-the-money: An option that is profitable if exercised immediately.
- Out-of-the-money: An option that is not profitable if exercised immediately.
- At-the-money: An option where the strike price is equal to the current market price of the underlying asset.
Strategies in Options Trading
The beauty of options trading lies in its versatility. A wide array of strategies exist‚ catering to diverse risk appetites and market outlooks. These strategies range from simple buy-and-hold approaches to complex‚ multi-leg trades involving multiple options contracts.
Covered Call Writing
This conservative strategy involves selling call options on shares you already own. It generates income through the option premium‚ but limits potential upside gains on the underlying stock. However‚ it provides some downside protection.
Protective Put Buying
This strategy involves buying put options on a stock you already own. It acts as insurance‚ limiting potential losses if the stock price declines. While this adds to the initial investment cost‚ it provides a safety net for long-term holders.
Straddles and Strangles
More advanced strategies like straddles and strangles involve buying both call and put options with the same expiration date‚ but different strike prices. These are suitable for investors who expect high volatility but are uncertain about the direction of price movement.
Risk Management in Options Trading
Options trading inherently carries substantial risk. The leverage inherent in options contracts magnifies both potential profits and losses. Effective risk management is paramount for successful and sustainable trading.
Understanding Leverage and Risk
Options offer leverage‚ meaning you can control a larger position with a smaller investment than with traditional stock trading. This leverage amplifies gains but also magnifies losses. A poorly managed trade can lead to significant financial setbacks.
Diversification and Portfolio Allocation
Diversification is a cornerstone of risk management. Don’t put all your eggs in one basket. Spread your investments across different assets and strategies to mitigate potential losses from any single position.
Position Sizing and Stop-Loss Orders
Careful position sizing‚ determining the appropriate amount to invest in each trade‚ is vital. Stop-loss orders automatically sell your position when the price reaches a predetermined level‚ limiting potential losses.
Factors Affecting Option Prices
Several factors influence option prices. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed trading decisions.
Underlying Asset Price
The price of the underlying asset is the most significant factor affecting option prices. As the underlying asset price changes‚ so do the prices of its associated options.
Time to Expiration
Options lose value as their expiration date approaches‚ a phenomenon known as time decay. The closer to expiration‚ the less time the option holder has to profit from price movement.
Volatility
Market volatility‚ or the degree of price fluctuation‚ significantly influences option prices. Higher volatility generally increases option prices‚ as there’s a greater chance of large price swings.
Interest Rates
Interest rates impact option pricing‚ particularly for longer-term options. Higher interest rates can increase the value of call options and decrease the value of put options.
Choosing a Broker for Options Trading
Selecting the right brokerage is paramount. Look for a broker offering a user-friendly platform‚ competitive commissions‚ robust research tools‚ and educational resources. Ensure the broker is regulated and reputable.
- Trading Platform: The platform should be intuitive and offer the tools you need for analysis and order execution.
- Commissions and Fees: Compare fees across different brokers to find the most cost-effective option.
- Research and Education: Access to quality research and educational materials can significantly aid your learning and trading success.
- Customer Support: Reliable customer support is crucial‚ especially when dealing with complex financial instruments.
Learning and Education in Options Trading
Options trading is a complex subject requiring continuous learning and refinement of skills. Don’t jump in without adequate preparation. Start with educational resources‚ practice with a paper trading account‚ and gradually increase your exposure to real-market trading.
Paper Trading and Simulated Accounts
Many brokers offer paper trading accounts‚ allowing you to practice trading without risking real money. This is an invaluable tool for honing your skills and testing strategies before committing capital.
Educational Resources and Courses
A plethora of educational resources are available‚ including online courses‚ books‚ and webinars. Leverage these resources to build a strong foundation in options trading theory and practice.
Mentorship and Community Support
Connecting with experienced traders through mentorship programs or online communities can provide valuable insights and support throughout your learning journey.
Options trading presents a world of opportunity‚ but it’s crucial to approach it with caution and a commitment to continuous learning. Start slowly‚ manage risk diligently‚ and celebrate small victories along the way. Successful options trading is a marathon‚ not a sprint‚ requiring patience‚ discipline‚ and a willingness to adapt to the ever-changing market dynamics. Remember to consult with a financial advisor before making any investment decisions. Thorough research and a well-defined trading plan are essential ingredients for long-term success in this challenging yet rewarding field. The potential for significant returns exists‚ but only with careful planning and execution. Never invest more than you can afford to lose.






